一、生态学重点学科简介
围绕生态与环境毒理学、污染防治与修复、生物质能源资源化转化等国家中长期发展的重大需求开展基础和应用基础研究。荣获安徽省科学技术奖(自然科学类)三等奖、淮南市科学技术奖三等奖和六安市青年科技进步奖各1项,获批淮南市创新团队3个、淮南师范学院科研创新团队1个。
团队成员先后主持国家级科研项目6项,省部级科研项目15项,厅局级科研项目29项。以第一作者或通讯作者在Environ Sci Technol、J Hazard Mater、Chemosphere、Sci Total Environ、Sci Rep等业内国际知名SCI期刊发表论文56篇,中文核心期刊论文150余篇。在典型重金属和有机污染物对动、植物的致毒效应机理与污染防治等领域取得了一定研究成果,其中水稻重金属污染的叶面阻断技术的应用研究已进入大田中试阶段。
二、研究方向
(1)环境与生态毒理学
围绕典型环境污染物对蚯蚓、线虫、农作物等致毒效应机理开展实验室研究,揭示了镉、铅、砷、抗生素、双酚A等典型无机和有机污染物的潜在毒性和致毒机理,为诊断和评价其生态风险性提供了科学依据。
(2)污染生态化学与污染防治
应用环境化学研究方法解析典型重金属、抗生素等污染物在土壤、水体以及农作物中的环境行为和归趋;研究典型纳米溶胶阻断土壤镉、铅等重金属在农作物中的迁移、富集及其潜在生态风险性和食品安全性,为消减农作物的重金属污染探寻新的防治途径。
(3)生物质能源资源化转化
筛选特异性高效菌株,结合微生物发酵工艺,探索应用这些菌株将农作物秸秆或中间代谢物进一步转化为有机能源。
三、学术队伍
现有成员21人,其中教授5人、副教授9人,拥有博士学位14人,硕士学位4人。现有安徽省教学名师2人,省优秀教师1人,安徽大学兼职硕士生导师2名,安徽省“特支计划”创新创业领军人才1人,校级教学名师2人,校级教坛新秀6人,校学科拔尖人才2名。
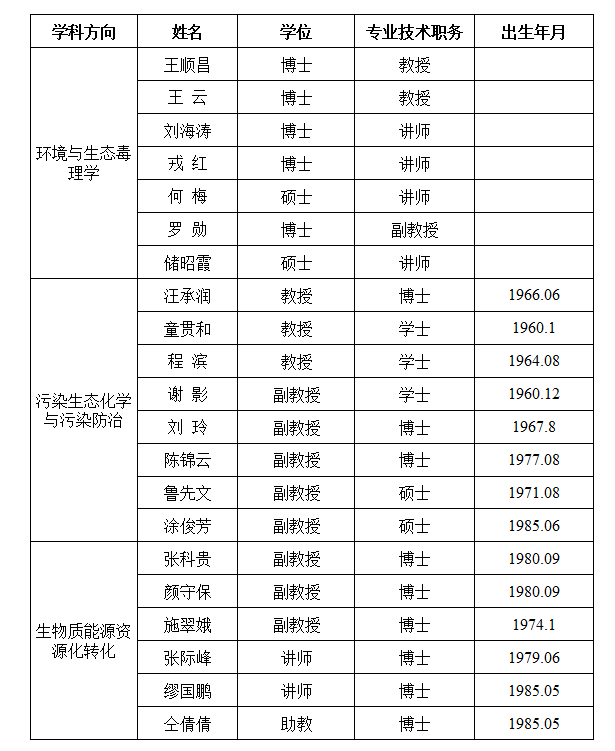
四、科学研究
先后主持国家级科研项目6项,省部级科研项目15项,厅局级科研项目29项。以第一或通讯作者发表SCI论文56篇,中文核心期刊论文150余篇,获批发明专利5项。荣获安徽省科学技术奖(自然科学类)三等奖、淮南市科学技术奖三等奖和六安市青年科技进步奖各1项,获批淮南市创新团队3个、淮南师范学院科研创新团队1个。
(一)科研项目
1、国家级项目
(1)稀土对植物作用的Hormesis效应的机理研究,国家自然科学基金面上项目(20877032),2008年,主持人:汪承润.
(2)PI3K途径介导的依赖于秀丽线虫p53的砷暴露细胞凋亡与增殖的分子机制研究,国家自然科学基金(21077040),2010年,主持人:王顺昌.
(3)三丁基锡对秀丽隐杆线虫的致毒机理研究,国家自然科学基金青年项目(20907016),2009年,主持人:王云.
(4)基于纤维素降解的牦牛瘤胃未培养微生物的功能研究、国家自然科学基金青年项目(31200007),2012年,主持人:张科贵.
(5)己酸二元发酵体系中甲烷菌促进己酸生成的机制研究,国家自然科学基金青年项目(项目编号:31501461),主持人:颜守保;
(6)转运蛋白TwPDR1在介导雷公藤甲素胞外分泌中的功能与磷酸化调控机制(31800256),国家自然科学基金青年项目,主持人:缪国鹏
2、省级科研项目
(1)基于秀丽线虫的水体微囊藻毒素毒性评价及其损伤信号传导,安徽省高校自然科学基金重大项目(ZD200909),主持人:王顺昌;
(2)基于秀丽线虫IGF-1R/PI-3K/AKT信号传导途径的砷诱导细胞凋亡和细胞周期停滞,安徽省自然科学基金项目(90413257),主持人:王顺昌;
(3)利用模式生物秀丽线虫评价微囊藻毒素的免疫毒性及其作用机制,安徽省高层次人才创新创业基金项目(2009Z62),主持人:王顺昌;
(4)硅硒溶胶在水稻富硒降镉中的应用基础研究,安徽省自然科学基金面上项目(1608085MB44),主持人:汪承润;
(5)水稻纳米富硒降镉的效应机理与应用研究,安徽省高等学校自然科学研究重大项目(KJ2015ZD37),主持人:汪承润;
(6)重金属非单调量效关系在土壤污染诊断中的应用基础研究,安徽省自然科学基金面上项目(1208085MB17),主持人:汪承润;
(7)重金属与碳纳米管的联合毒性效应、作用机理及安全性评价,污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室开放课题资助项目(PCRRF10020),主持人:汪承润;
(8)外源稀土促进植物体抗氧化胁迫的微观机理研究,污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室开放课题资助项目(PCRRF08011),主持人:汪承润;
(9)秀丽线虫中细胞核RNA干扰造成的染色体修饰,安徽省自然科学基金项目(1608085MC68),主持人:王云;
(10)秀丽线虫中siRNA对染色质修饰与细胞凋亡的调控机制,中国博士后科学基金(2015M582006),主持人:王云;
(11)基于纤维素降解的牦牛瘤胃未培养微生物的功能研究,安徽省自然科学基金面上项目(1308085MC31),主持人:张科贵;
(12)转录因子TwTGAP1在雷公藤内酯醇生物合成中的功能与应用,安徽省自然科学基金项目(1708085QC52),主持人:缪国鹏;
(13)水鸟群落特征对沿淮湿地生境变化响应机制,安徽省自然科学基金项目(1408085MC51),主持人:陈锦云;
(14)大气CO2和O3浓度升高对底泥微生物分子多态性变化的影响,污染控制与资源化研究国家重点实验室研究项目(PCRRF12014),主持人:施翠娥;
(15)己酸二元发酵体系研究(2013SQRL070ZD),安徽省高校省级优秀青年人才基金重点项目,主持人:颜守保;
(16)己酸二元体系发酵机理研究(1508085QC56),安徽省自然科学基金项目,主持人:颜守保;
(17)酿酒丢糟资源化综合利用关键技术研究(1804a07020122),安徽省重点研究与开发计划项目,主持人:颜守保。
3、厅局级科研项目
(1)轻稀土在防治蔬菜病害和促进农药降解中的应用及其生理机制的研究(2005KJ197),安徽省高校自然科学基金项目,主持人:汪承润;
(2)典型工业化废水的生态毒性监测与安全性评价技术(KJ2012Z381),安徽省高校省级自然科学产学研项目,主持人:汪承润;
(3)淮河与巢湖水质污染对淡水鱼类的毒性效应(KJ2008B200),安徽省高校自然科学研究项目,主持人:王云;
(4)反刍动物瘤胃微生物混合培养体系对纤维素的降解(KJ2010B201),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金项目,主持人:张科贵;
(5)转运蛋白TwPDR1在雷公藤甲素胞外分泌中的功能验证(KJ2016A668),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金重点项目,主持人:缪国鹏;
(6)基于二级食物链水平环境因子作用下的纳米银毒性效应研究(KJ2018A0471),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金重点项目,主持人:罗勋;
(7)猫听觉中枢初级听皮层GABA受体表达的年龄相关性比较研究(KJ2009B156),安徽省教育厅自然科学研究项目,主持人:罗勋;
(8)整合组学数据预测肝癌关键基因及其致病机制研究(KJ2013B259),安徽省教育厅自然科学研究项目,主持人:张际峰;
(9)基于生物网络筛查肝癌易感基因研究(gxyqZD2016264),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金重点项目,主持人:张际峰;
(10)利用煤矸石、油菜秸秆等废弃资源开发蔬菜有机生态型无土栽培及产业化生产技术(KJ2009A115),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金重点项目,主持人:童贯和;
(11)模拟酸雨对淮南地区农作物的伤害研究(2003kj020zc),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金项目,主持人:童贯和;
(12)筛选拮抗黄曲霉的黑曲霉突变株及活性物质的分离纯化(KJ2010B207),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金项目,主持人:施翠娥;
(13)煤矿塌陷区生态恢复模式对土壤微生物多样性变化的影响(KJ2015A279),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金重点项目,主持人:施翠娥;
(14)2016年高校优秀中青年骨干人才国内外访学研修重点项目(gxfxZD2016205),安徽省人事厅,主持人:施翠娥;
(15)多类型生物炭重组蚯蚓堆肥体系对污泥中重金属稳定的效应及其机制研究(KJ2018A0473),安徽省高等学校自然科学研究重点项目,主持人:储昭霞;
(16)玉竹茎、叶药物成分分析(2003KJ296),安徽省教育厅自然科学基金一般项目,主持人:程滨;
(17)菊酯作用下的小菜蛾差异表达蛋白分析(KJ2008A007),安徽省教育厅自然科学研究重点项目,主持人:程滨;
(18)UV辐射诱导的秀丽线虫延迟损伤效应研究(2012SQRL178),安徽省教育厅青年基金项目,主持人:何梅;
(19)用植物抗氧化系统评价重金属对小麦幼苗的污染与毒性(KJ2007B341ZC),安徽省教育厅自然科学研究项目,主持人:鲁先文;
(20)模拟酸雨和重金属离子单一几复合胁迫对油菜幼苗生长和抗氧化酶活性影响的研究(KJ2009B267Z),安徽省教育厅自然科学研究项目,主持人:鲁先文;
(21)瘤胃微生物混合培养体系降解农作物秸秆产可再生能源的研究(2012A01004),淮南市科技局科技计划项目,主持人:张科贵;
(22)基于人工纳米材料沿食物链传递的生态毒理学效应研究(2012A01008),淮南市科技局科技计划项目,主持人:罗勋;
(23)轻稀土在防治蔬菜病害和促进农药降解中的应用(2004197),淮南市科技局科技计划项目,主持人:汪承润;
(24)典型工业化废水的生态安全性监测与评价的方法和技术(2011A08010),淮南市科技局科技计划项目,主持人:汪承润;
(25)淮南市城市水系治理生物多样性监测项目,淮南市发改委及亚洲开发银行,主持人:陈锦云, 2013年;
(26)安徽G312国道淠河大桥改建工程生态影响专题报告,六安市林业局,主持人:陈锦云,2016年;
(27)大唐发电泾县纪村水电站增效扩容工程生态影响专题报告,泾县水利局,主持人:陈锦云,2018年;
(28)淮南市生物多样性专项调查,淮南市林业局,主持人:陈锦云,2018年;
(29)横排头水利工程除险加固工程对淠河国家级湿地公园生态影响专题评估,淠史杭管理总局,主持人:陈锦云,2018年.
(二)SCI论文
(1)Wang SC, Chu ZX, Zhang KG, et al. Cadmium-induced serotonergic neuron and reproduction damages conferred lethality in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 213: 11-18.
(2)Wang S, Teng X, Wang Y, Yu HQ, Luo X, Xu A, Wu L. Molecular control of arsenite-induced apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans: Roles of insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling pathway [J]. Chemosphere, Chemosphere, 2014, 112: 248–255.
(3)Wang S, Geng Z, Wang Y, Tong Z, Yu H. Essential roles of p53 and MAPK cascades in microcystin-LR-induced germline apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 2012, 46: 3442-3448.
(4)Wang S, Geng Z, Yu Y, Guo J. Arsenite exposure induces oxidative stresses in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Information Technol Agricul Engineer, 2012, 134: 911-918.
(5)Wang SC, Wu LJ, Wang Y, et al. Copper-induced germline apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans: The independent roles of DNA damage response signaling and the dependent roles of MAPK cascades [J]. Chem-Biol Interact, 2009, 180: 151-157.
(6)Wang S, Tang M, Pei B, et al. Cadmium induced germline apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans: the roles of HUS1, p53 and MAPK signaling pathways [J]. Toxicol Sci, 2008, 102: 345-351.
(7)Wang SC, Zhao Y, Wu LJ, et al. Induction of germline cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by sodium arsenite in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Chem Res Toxicol, 2007, 20: 181-186.
(8)Rong H, Wang CR, Yu XR, et al. Carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes exacerbated oxidative damage in roots of Vicia faba L. seedlings under combined stress of lead and cadmium [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 161: 616-623.
(9)Wang CR, Rong H, Liu HT, et al. Detoxification mechanisms, defense responses, and toxicity threshold in the earthworm Eisenia foetida exposed to ciprofloxacin-polluted soils [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 612: 442-449.
(10)Wang CR, Liu HT, Chen JY, et al. Carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes aggravated biochemical and subcellular damages in leaves of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) seedlings under combined stress of lead and cadmium [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 274: 404-412.
(11)Wang CR, Wang QY, Tian Y, et al. Lanthanum ions intervened in enzymatic production and elimination of reactive oxygen species in leaves of rice seedlings under cadmium stress [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2014, 33 (7): 1656-1664.
(12)Wang CR, Xiao JJ, Tian Y, et al. Antioxidant and prooxidant effects of lanthanum ions on Vicia faba L. seedlings under cadmium stress, suggesting ecological risk [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2012, 31 (6): 1355-1362.
(13)Wang CR, Luo X, Tian Y, et al. Biphasic effects of lanthanum on Vicia faba L. seedlings under cadmium stress, implicating finite antioxidation and potential ecological risk [J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 86: 530-537.
(14)Wang CR, Zhang KG, He M, et al. Mineral nutrient imbalance, DNA lesion and DNA-protein crosslink involved in growth retardation of Vicia faba L. seedlings exposed to lanthanum ions [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24 (2): 214-220.
(15)Wang CR, Gu XY, Wang XR, et al. Stress response and potential biomarkers in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) seedlings exposed to soil lead [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011, 74: 41-47.
(16)Wang CR, Tian Y, Wang XR, et al. Hormesis effects and implicative application in assessment of lead-contaminated soils in roots of Vicia faba seedlings [J]. Chemosphere, 2010, 80: 965-971.
(17)Wang CR, Tian Y, Wang XR, et al. Lead-contaminated soil induced oxidative stress, defense response and its indicative biomarkers in roots of Vicia faba seedlings [J]. Ecotoxicology, 2010, 19: 1130-1139.
(18)Wang CR, wang XR, Tian Y, et al. Oxidative stress, defense response and early biomarkers for lead-contaminated soil in Vicia faba seedlings [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2008, 27 (4): 970-977.
(19)Wang CR, Wang XR, Tian Y, et al. Oxidative stress and potential biomarkers in tomato seedlings subjected to soil lead contamination [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2008, 71: 685-691.
(20)Wang CR, Lu XW, Tian Y, et al. Lanthanum resulted in unbalance of nutrient elements and disturbance of cell proliferation cycles in V. faba L. seedlings [J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2011, 143: 1174-1181.
(21)Xu XH, Huang ZC, Wang CR*, et al. Toxicological effects, mechanisms, and implied toxicity thresholds in the roots of Vicia faba L. seedlings grown in copper-contaminated soil [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22: 13858-13869.
(22)Wang CR, He M, Shi W, et al. Toxicological effects involved in risk assessment of rare earth lanthanum on roots of Vicia faba L. seedlings [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23 (10): 1721-1728.
(23)Wang CR, Shi CE, Liu L, et al. Lanthanum element induced imbalance of mineral nutrients, HSP 70 production and DNA-protein crosslink, leading to hormetic response of cell cycle progression in root tips of Vicia faba L. seedlings [J]. Dose-Response, 2012, 10: 96-107.
(24)Wang N, Wang CR*, Bao X, et al. Toxicological effects and risk assessment of lanthanum ions on leaves of Vicia fabaL. Seedlings [J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2011, 29 (10): 997-1003.
(25)Wang Y, Zhang L, Luo X, et al. Bisphenol A exposure triggers apoptosis via three signaling pathways in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7 (52): 32624-32631.
(26)Wang Y, Luo X, Yan S, et al. Using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model animal for assessing the toxicity induced by Tributyltin [C]. 2016 International Conference on Material, Energy and Environment Engineering, 2016, 102-109.
(27)Wang Y, Wang S, Luo X, et al. The roles of DNA damage-dependent signals and MAPK cascades in tributyltin-induced germline apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 108: 231-238.
(28)Wang Y, Jian FL, Wu JY, et al. Stress-response protein expression and DAF-16 translocation were induced in tri-n-butyltin-exposed Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2012, 89: 704-711.
(29)Wang Y, Zheng RH, Zuo ZH, et al. Relation of hepatic EROD activity and cytochrome P4501A level in Sebastiscus marmoratus exposed to benzo [a] pyrene [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2008, 20(1): 101-104.
(30)Zhang KG, Song L, Dong XZ. Selenomonas bovis sp. nov., isolated from yak rumen contents [J]. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2009, 59: 2080-2083.
(31)*Zhang KG, Dong XZ. Proteiniclasticum ruminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic proteolytic bacterium isolated from yak rumen [J]. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2010, 59: 2221-2225.
(32)Yan SB, Chen XS, Wu JY, et al. Pilot-scale production of fuel ethanol from concentrated food waste hydrolysates using Saccharomyces cerevisiae H058 [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2013, 36 (7): 937-946.
(33)Yan SB, Chen XS, Wu JY, et al. Ethanol production from concentrated food waste hydrolysates with yeast cells immobilized on corn stalk [J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 94 (3): 829-838.
(34)Yan SB, Li J, Chen XS, et al. Enzymatical hydrolysis of food waste and ethanol production from the hydrolysate [J]. Renewable Energy, 2011, 36 (4): 1259-1265.
(35)Yan SB, Wang PC, Zhai ZJ, et al. Fuel ethanol production from concentrated food waste hydrolysates in immobilized cell reactors by Saccharomyces cerevisiae H058 [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2011, 26 (5): 731-738.
(36)Yan SB, Tang HJ, Wang SC, et al. Improvement of kojic acid production in Aspergillus oryzae B008 mutant strain and its uses in fermentation of concentrated corn stalk hydrolysate [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2014, 37 (6): 1095-1103.
(37)Yan SB, Wang SC, Wei GG, et al. Investigation on the main parameters during the fermentation of Chinese Luzhou-flavor liquor [J]. Journal of the Institute of Brewing, 2015, 121: 145-154.
(38)Miao GP, Han J, Zhang JF, et al. A MDR transporter contributes to the different extracellular production of sesquiterpene pyridine alkaloids between adventitious root and hairy root liquid cultures of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook . f [J]. Plant Mol Bio, 2017, 95 (1-2): 51-62.
(39)Miao GP, Han J, Zhang KG, et al. Protection of melon against Fusariumwilt-root knot nematode complex by endophytic fungi Penicillium brefeldianum HS-1 [J]. 2018 (online). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-018-0565-0.
(40)Miao GP, Han J, Wang CR, et al. Growth inhibition and induction of systemic resistance against Pythium aphanidermatum by Bacillus simplex strain HS-2 [J]. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 2018, online.
(41)Miao GP, Zhu CS, Feng JT, et al. Effects of plant stress signal molecules on the production of wilforgine in an endophytic actinomycete isolated from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f [J]. Curr Microbiol, 2015, 70 (4): 571-579.
(42)Miao GP, Zhu CS, Yang Q, et al. Elicitation and in situ adsorption enhanced secondary metabolites production of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. adventitious root fragment liquid cultures in shake flask and a modified bubble column bioreactor [J]. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng, 2014, 37 (4): 641-650.
(43)Miao GP, Li W, Zhang B, et al. Identification of genes involved in the biosynthesis of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f [J]. Secondary metabolites by suppression subtractive hybridization [J]. Plant Mol Biol Rep, 2014, 33 (4): 756-769.
(44)Miao GP, Zhu CS, Feng JT, et al. Aggregate cell suspension cultures of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f. for triptolide, wilforgine, and wilforine production [J]. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 2013, 112: 109-116.
(45)Luo X, Xu SM, Yang YN, et al. Insights into the ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles transferred from Escherichia coli to Caenorhabditiselegans [J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36465.
(46)Luo X, Xu SM, Yang YN, et al. A novel method for assessing the toxicity of silver nanoparticles in Caenorhabditiselegans [J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 168: 648-657.
(47)Luo X, Xu SM, Yang YN, et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes induced the developmental abnormality of C. elegans [J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol, 2016, 16: 1-7.
(48)Zhang JF, Nie LW, Wang Y, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the large-headed frog, Limnonectes bannaensis (Amphibia: Anura), and a novel gene organization in the vertebrate mtDNA [J]. Gene, 2009, 442: 119-127.
(49)Zhang JF, Wang X, Tian WD, et al. Evidence of positive selection on D-lactate dehydrogenases in Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus [J]. IET Systems Biology, 2015, 9 (4): 172-179.
(50)Tong QQ, Zhou YH, Chen XS, et al. Genome shuffling and ribosome engineering of Streptomyces virginiae, for improved virginiamycinproduction [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2018 (41): 729-738.
(51)Shi CE, Wang C, Xu XN, et al. Comparison of bacterial communities in soil between nematode-infected and nematode-uninfected Pinus massoniana pinewood forest [J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2014, 85: 11-20.
(52)Shi CE, Pan L, Wang CR, et al. Facile preparation of Ag/NiO composite nanosheets and their antibacterial activity [J]. JOM, 2016, 68 (1): 324-329.
(53)Rong H, TangYY, Zhang H, et al. The Stay-Green Rice like (SGRL) gene regulates chlorophyll degradation in rice, J Plant Physiol, 2013, 170 (15): 1367-1373.
(54)Chu ZX, Wang XM, Wang YM, et al. Effects of coal spoil amendment on heavy metal accumulation and physiological aspects of ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) growing in copper mine tailings [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190: 36.
(55)Chen J, Pan T, Hu L, et al. Mitochondrial genome of the Emberiza rustica (Emberizidae: Emberiza) [J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 2014, 25 (4): 284-285.
(56)Cheng B, Hu CW, Zhao YJ, et al. Effects of plants development and pollutant loading on performance of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands [J]. Int J Environ Sci tec, 2011, 8 (1): 177-186.
(57)Cheng B, Ge ZG, Zhang H, et al. Nutrient removal and biogas upgrading by microalgal strains cultured in anaerobic digested starch wastewater [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2016, 91: 3028-3034.
(三)发明专利
(1)汪承润. 一种甄别和评价复杂成分工业废水遗传毒性的方法和技术. 授权号: 201310034237.7, 2015年.
(2)张际峰. 一种基于miRNA序列分析物种进化的方法. 专利号: ZL201510579620.X, 2017年.
(3)张际峰. 一种用于预测癌症病人预后相关的蛋白质对的方法. 专利号: ZL201510598608.3, 2017年.
(4)仝倩倩. 一种卧式内外双循环气升式生物反应器. 专利号: CN 205635573 U[P]. 2016年.
(5)仝倩倩. 一种提高维吉尼亚链霉菌发酵生产VGM产量的方法. 专利号: CN 105907822 A[P], 2016年.
(四)获奖
(1)汪承润. 安徽省科学技术奖(自然科学类)三等奖(D1),2018年
(2)张际峰. 淮南市科技进步奖三等奖(R1), 2016年
(3)王顺昌. 安徽省高校教学名师奖, 2014年
(4)汪承润. 安徽省高校教学名师奖, 2015年
(五)学术交流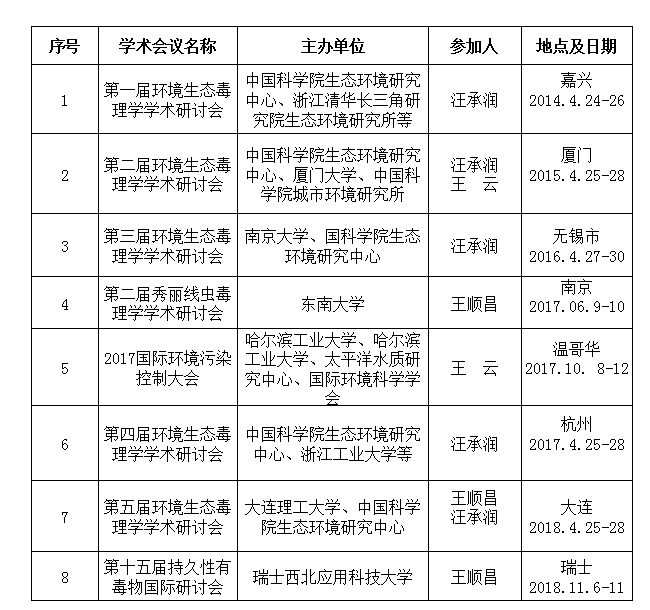
五、服务社会与人才培养
(一)服务社会
本学科与淮南市林检局、安徽省林业厅、凤台县林业局等单位签订林业有害生物普查政府购买服务项目,获取项目资金20余万元,项目进展顺利,已通过三次中检。
2016年6月,本学科作为独立第三方,参与淮南市飞防美国白蛾项目验收工作。
本学科与潘集区亚鹏盛农有限公司合作,基本解决了抗酥瓜重茬病的难题,该项技术对促进地方经济的发展将发挥重要作用。2015年,在淮南市第四季度经济调度会上,受到市委书记沈强的关注。本季抗重茬酥瓜已经收获,亩产4000余公斤,品质良好,深受瓜农的高度称赞。
本学科将进一步拓展服务领域,向生物技术外包服务、第三方检测、食品安全、生态沼气池建设等方向拓展,更好地服务地方经济的发展。
(二)人才培养
